Time and day
A period of duration measured by the apparent movement of celestial bodies about the earth. Period of time elapsing between two successive transits of heavenly body over the same meridian is called a day.
Zone time systems at sea
World divided into 24 zones of 150 each. Center of the system is Greenwich. Centre division lies between meridian of 7 1/20 E and 7 1/20 W (Zone 0 or Z, where we get Zulu time). Zones lying Eastward of Greenwich are numbered in sequence up to 12 and prefixed with (-) also correspond with A to M (J is omitted). Westward zones are prefixed with (+) also correspond with N to Y.
Zone time on land is known as standard time. Standard time followed by country can be found by referring following books.
1. NP 286 (2), ALRS Vol 2
2. Nautical Almanac
3. Admiralty Tide Table
For example Sri Lanka is in Zone E/ F, 5 1/2 hours ahead of GMT. If Zulu time is 1200 hours, Zone or local time in Sri Lanka is represented as 1200 (+5 1/2 hours)
Conversion of longitude arc into zone.
To convert longitude arc into zone divide longitude by 15 if remaining less than 7 1/20 ignore it. If higher add one. If longitude in east prefix will be (-) and if longitude in west prefix will be (+) respectively.
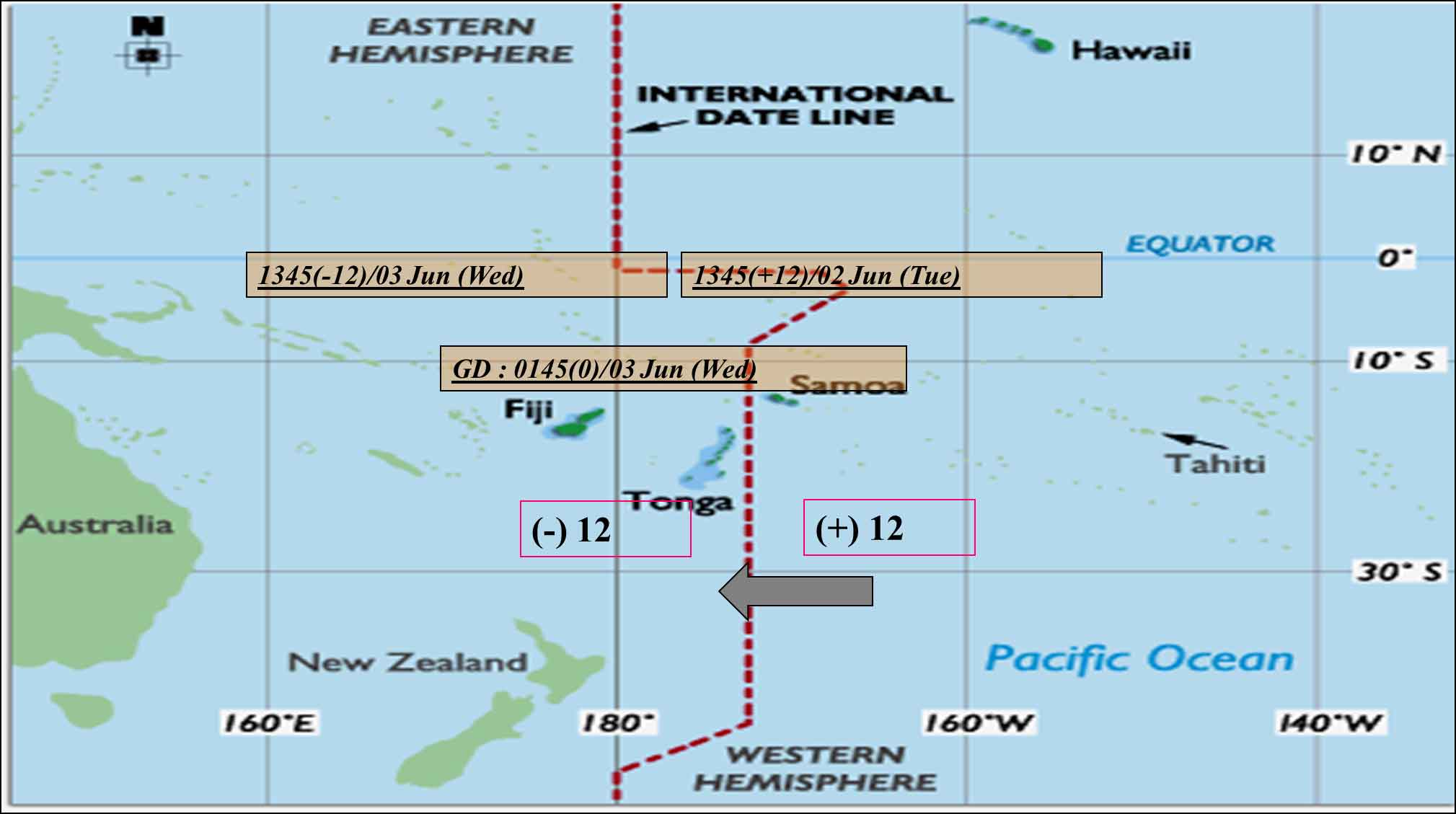
International Date Line (IDL)
When IDL crossed on an Easterly course date is put Back a Day. When IDL is crossed on a westerly course date is put on a Day.
i.e. - When crossing from East to West you will lose a day.